Scaling microservices is typically an example of horizontal scaling.
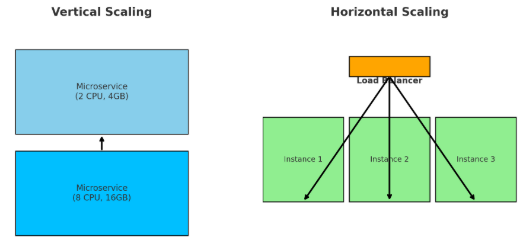
Here’s a diagram that demonstrates Vertical Scaling vs Horizontal Scaling in microservices :
- Left → Vertical scaling (same service, bigger machine).
- Right → Horizontal scaling (multiple service instances behind a load balancer).
Here’s why:
- Horizontal Scaling (Scale-Out) → You add more instances (containers, pods, VMs) of the microservice and distribute the load using a load balancer or service mesh.
- Example: Running 10 replicas of your “Order Service” in Kubernetes instead of just 2.
- Microservices are designed to run independently and scale out based on demand.
- Vertical Scaling (Scale-Up) → You increase the resources (CPU, RAM, storage) of the same instance.
- Example: Increasing a single service container’s CPU from 2 cores to 8 cores.
Summary
👉 Microservices architecture favors horizontal scaling.